
Not Recommended Easy To Use 3 D Colored Surface Plotter Matlab Ezsurf Mathworks France
\text {such that} ;Y \geq 0 ;
Laplacian of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2)
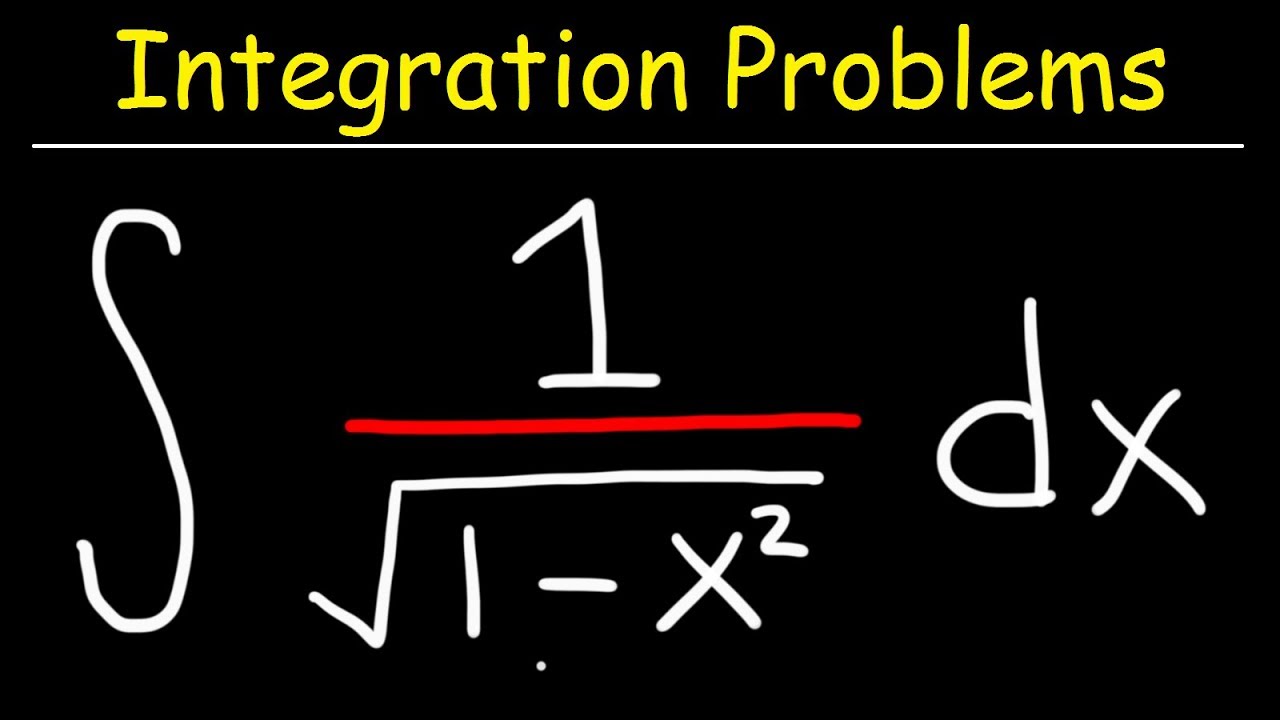
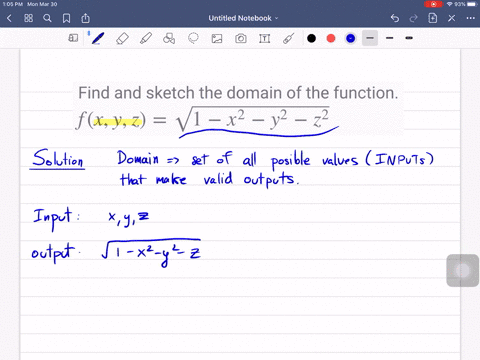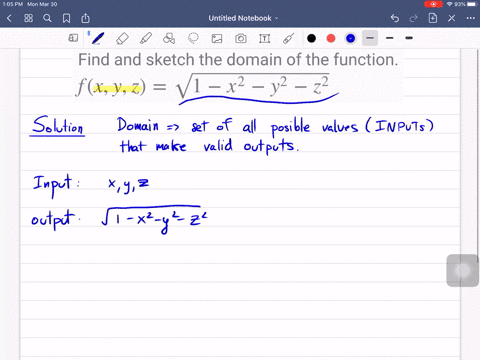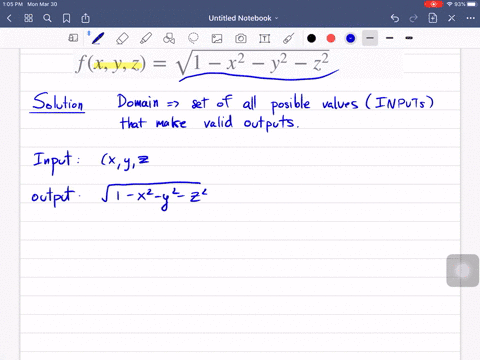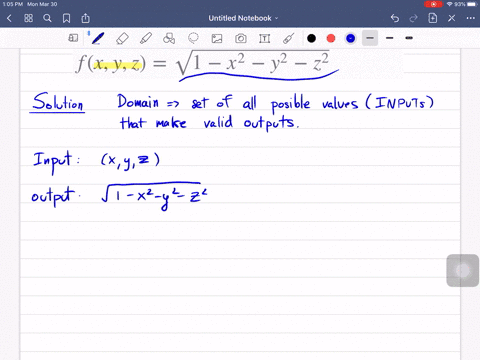
Laplacian of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2)-Think about how you'd find the domain of a function with one variable, like f (x)=1/x or g (x)=sqrtx The same idea applies, the term under the square root can't be negative, ie 25x 2 y 2 z 2 >=0 So 25>So, just like 5 (a b) = 5 a 5 b, a 2 b 2 = a 2 b 2 = a b 5(ab) = 5a 5b, \sqrt{a^2 b^2} = \sqrt{a^2} \sqrt{b^2} = a b 5 (a b) = 5 a 5 b, a 2 b 2 = a 2 b 2 = a b Why some people say it's false The distributive property doesn't work for the square root functions, so you can't say that a 2 b 2 = a 2 b 2 \sqrt{a
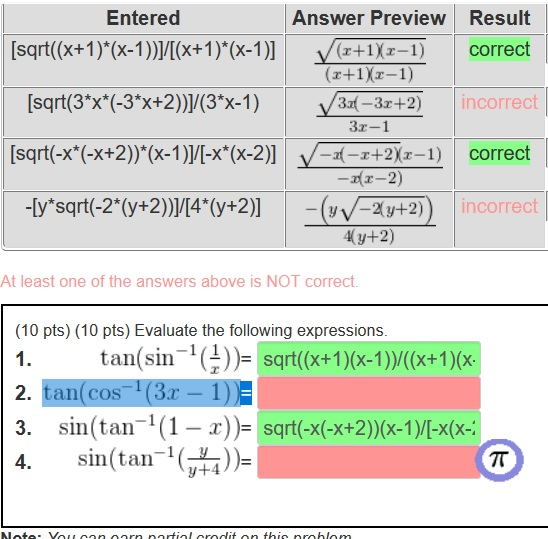
Solved Answer Preview Result Sqrt X 1 X1 I X 1 X1 1 Chegg Com
If we let `z=1` in `z=sqrt(x^2y^2)`, we eventually arrive at `x^2y^2=1`, which is a circle of radius 1, which we sketch at a height of `z=1` If we let `z=2` in `z=sqrt(x^2y^2)`, we eventually arrive at `x^2y^2=4`, which is a circle of radius 2, which we sketch at a height of `z=2`Easy as pi (e) Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math InputIf x 2 4y 2 3z 2 \(\frac{19}{4}=2\sqrt{3}(xyz)\), then the value of (x 4y 3z) is This question was previously asked in SSC CHSL Official Paper 19 (Held on 5
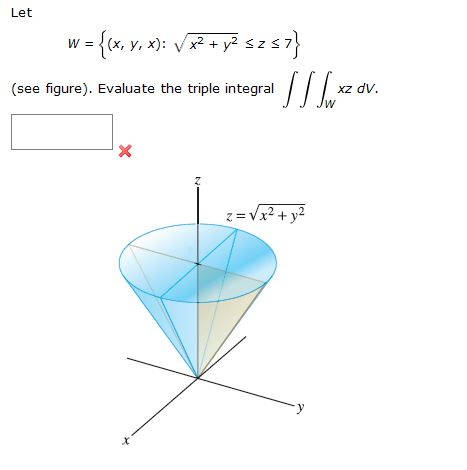
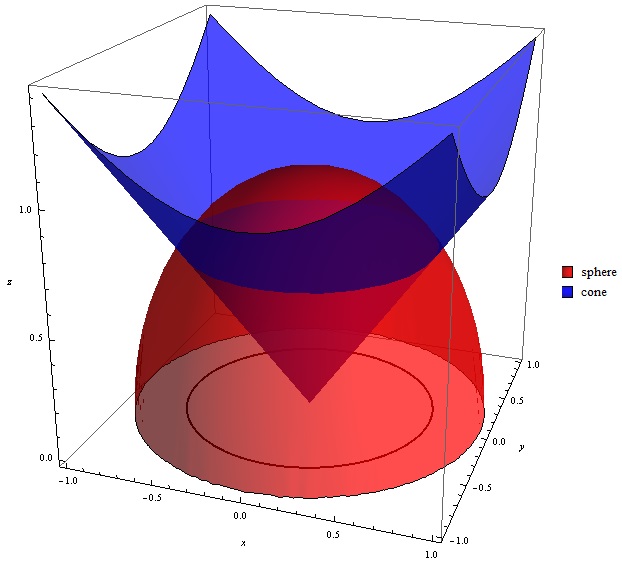
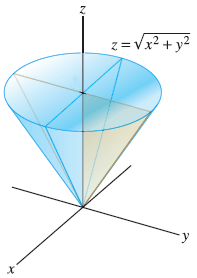
Figure 2 Part of the region S bounded by x2z2 = a2 and x2 y2 = a2 for x ≥ 0 Note that the projection of region S1 on the y − z plane, call it R is a a square 0 ≤ y ≤ a, 0 ≤ z ≤ a We breakPiece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math Input Use Math Input Mode to directly enter textbook math notationOkay, So this is your x six then because your ex ex you Y Y U Z Z Because the function you is symmetric in terms of X, Y Or Z So by the same procedure we will find you Why why should be equal to negative O Negative two Y square plus X square class This square over X square plus Y square plus the square through the 5/2 And U Z Z will
Laplacian of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2)のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 | 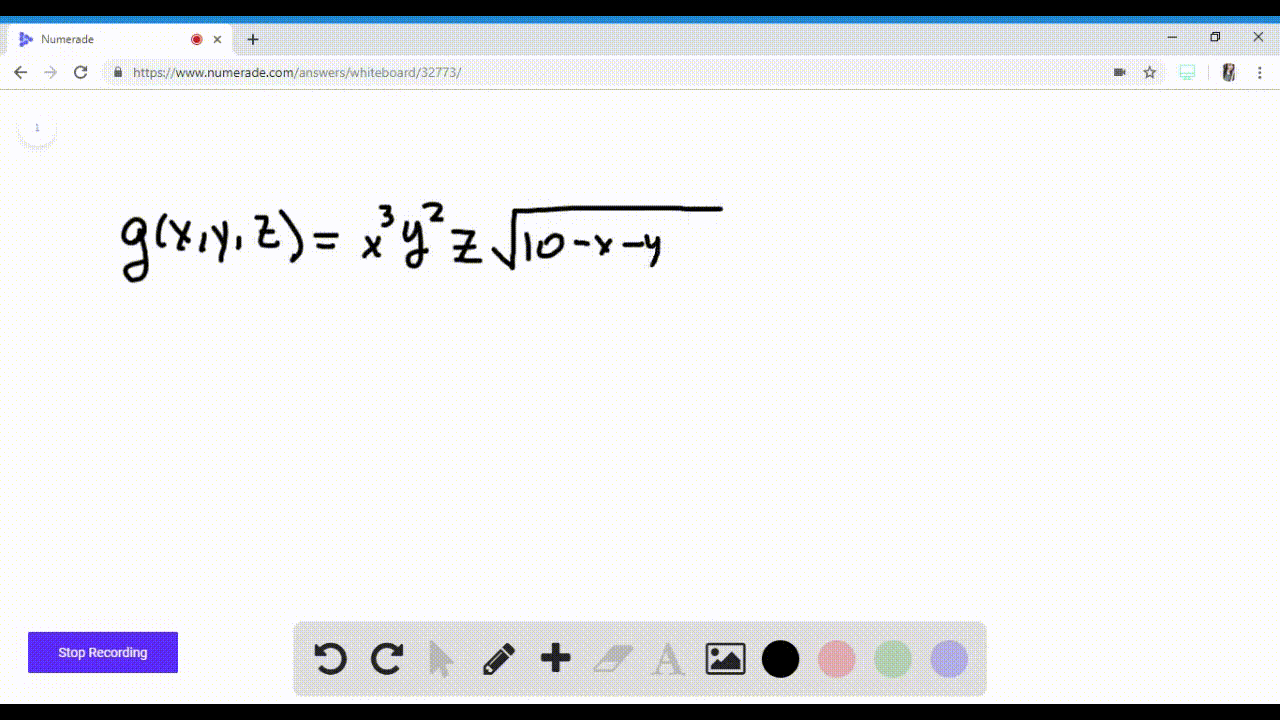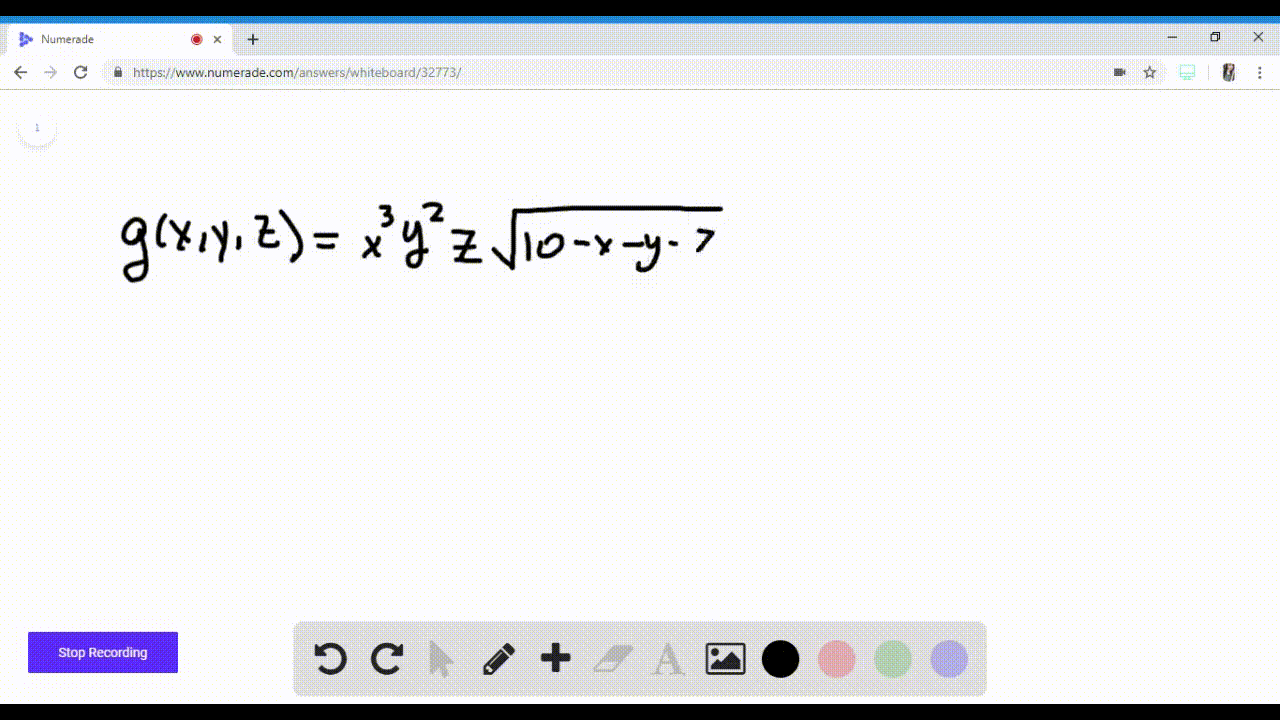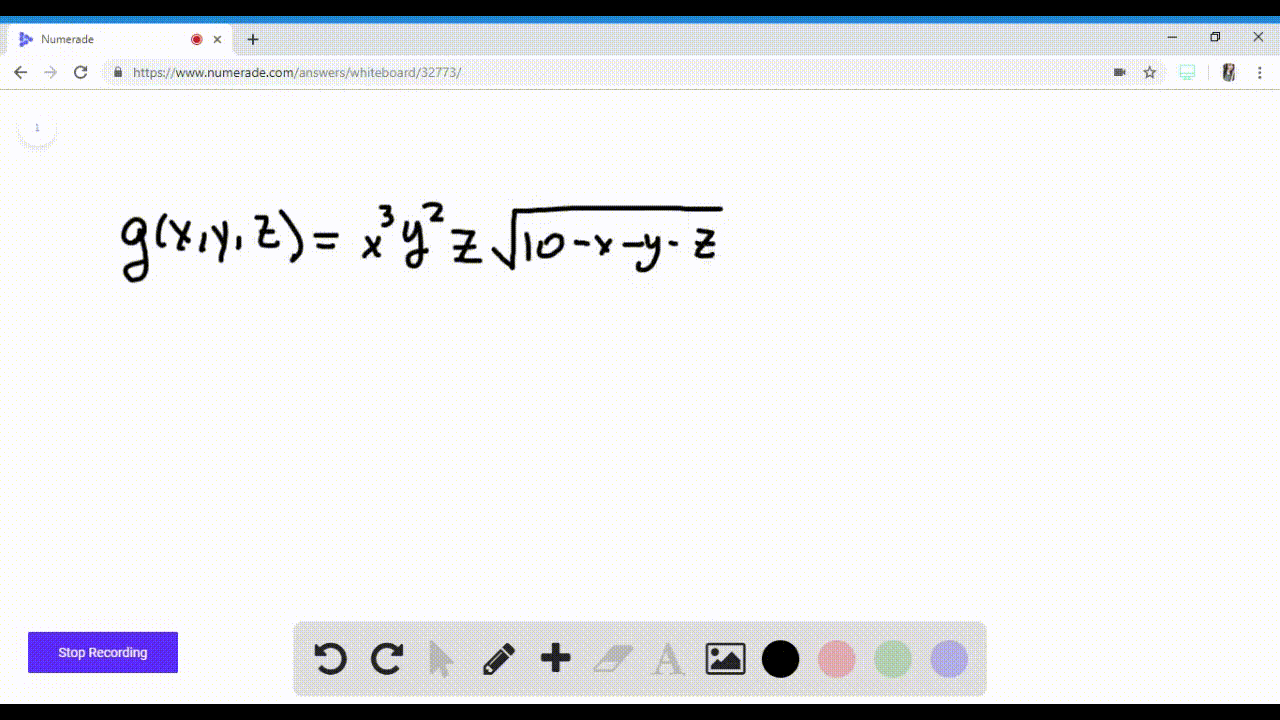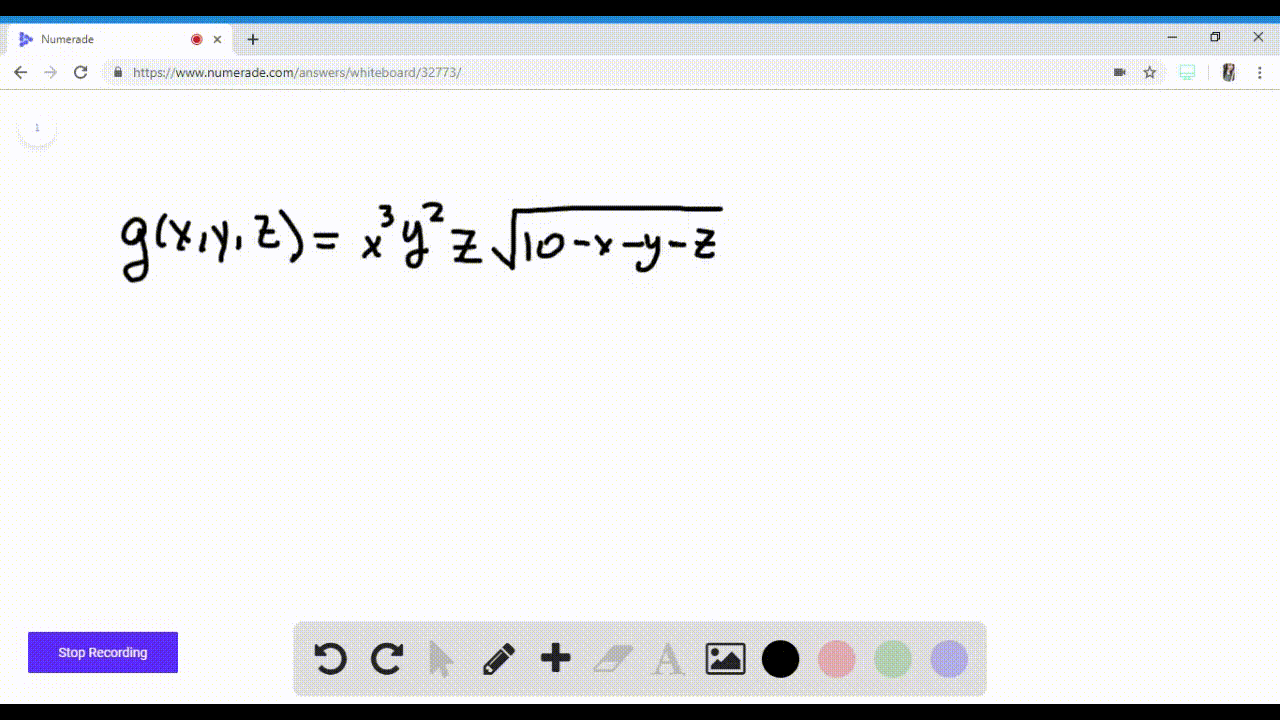 1 |  1 |
 1 | 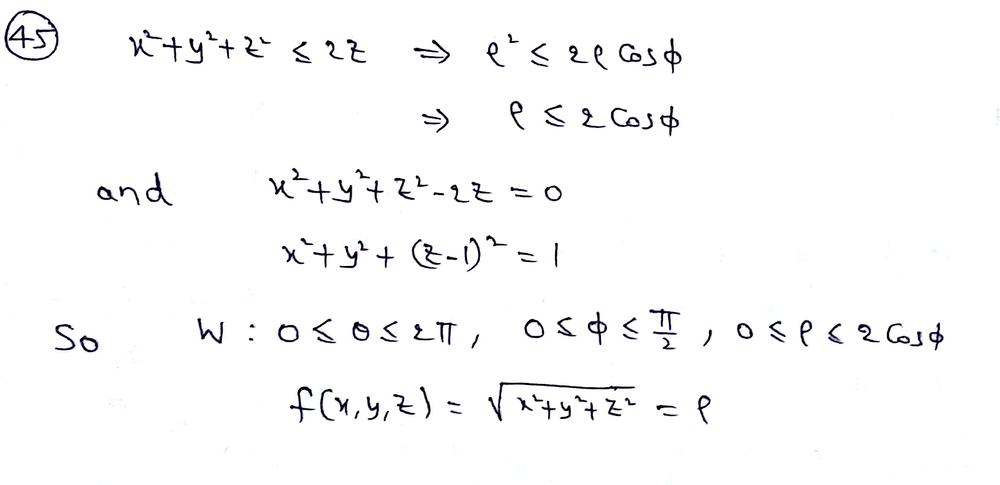 1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
1 | 1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 | 1 |
1 | 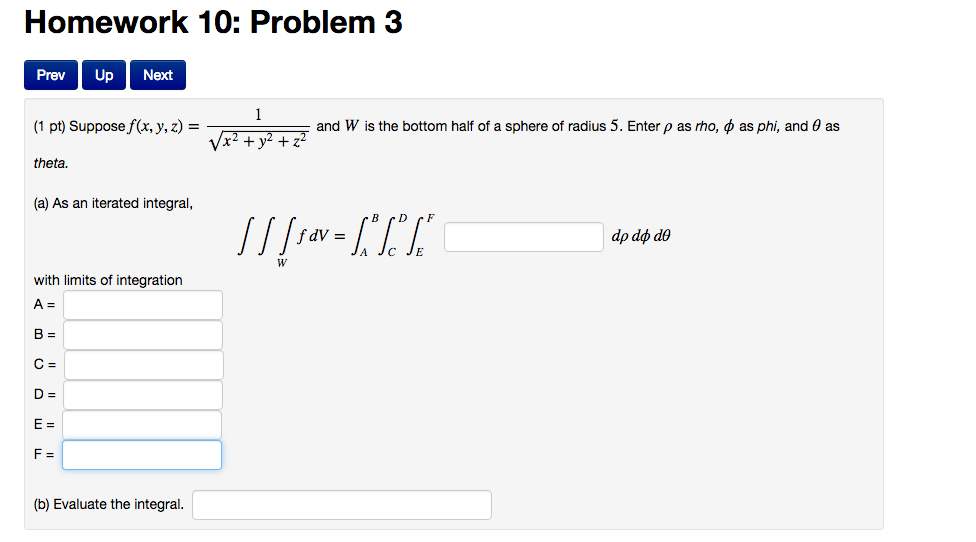 1 | 1 |
 1 |  1 | 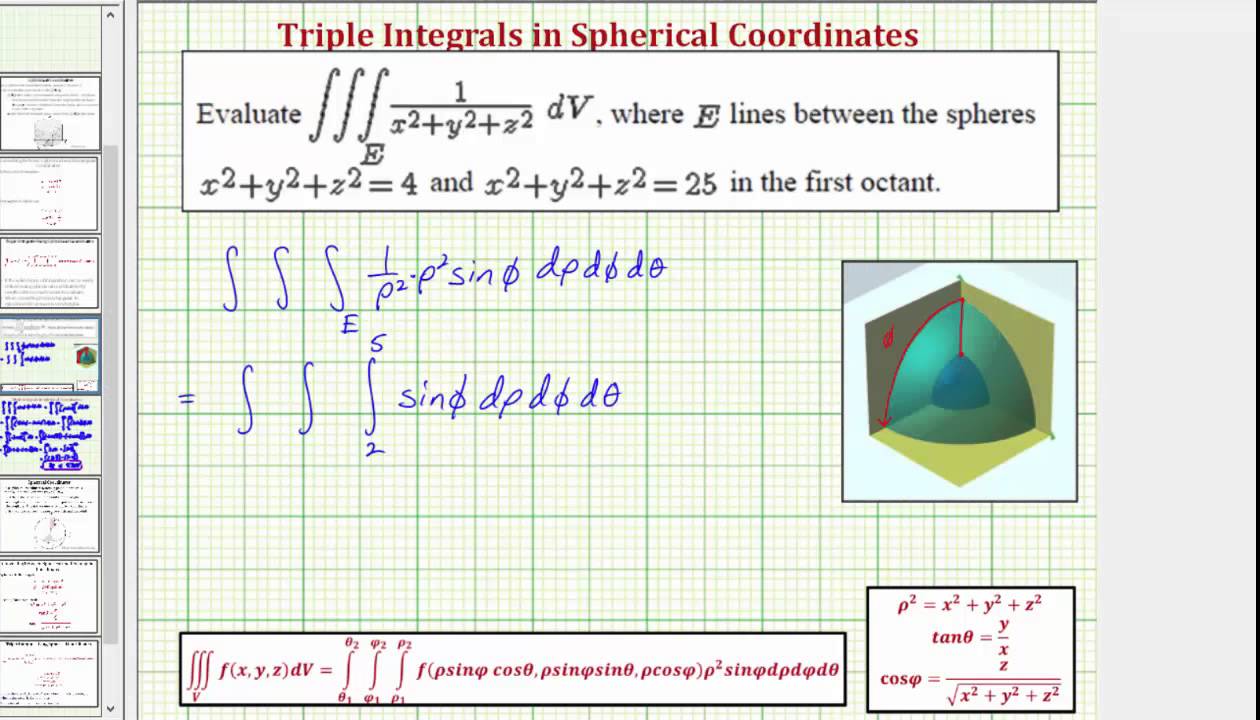 1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
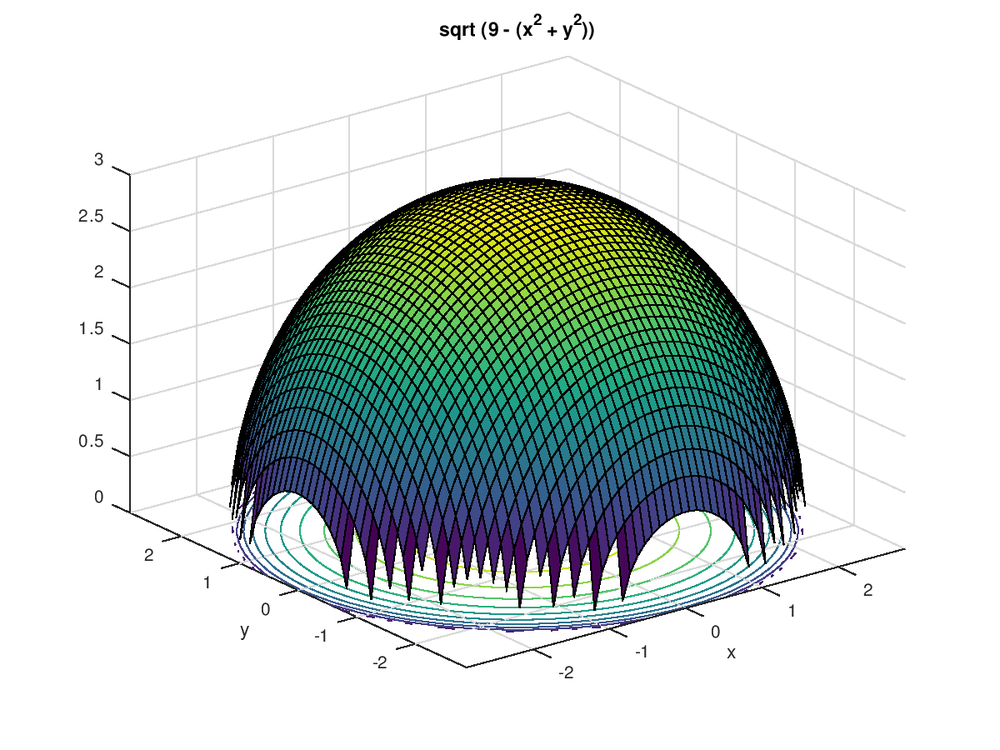 1 | 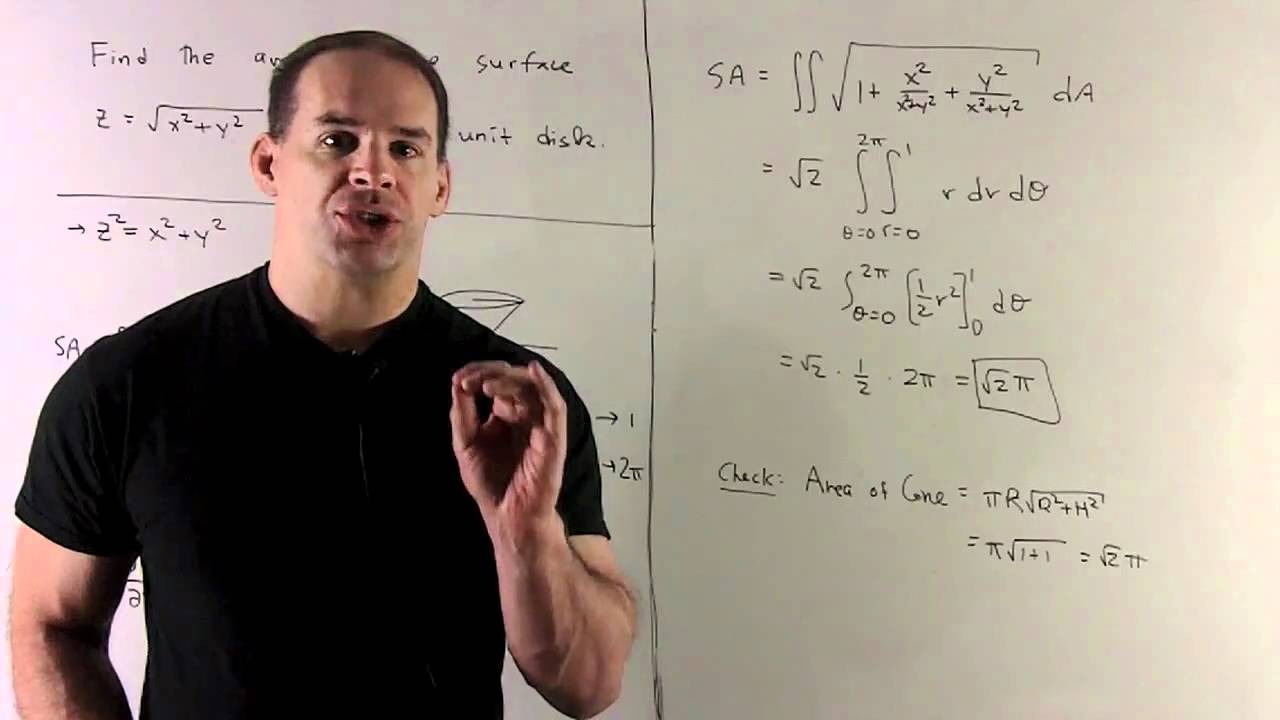 1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 | 1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
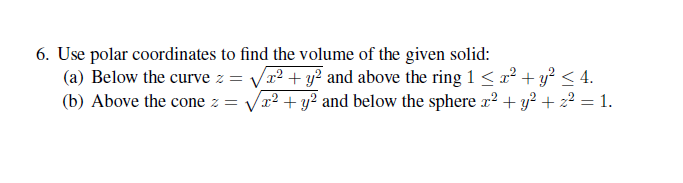 1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 | 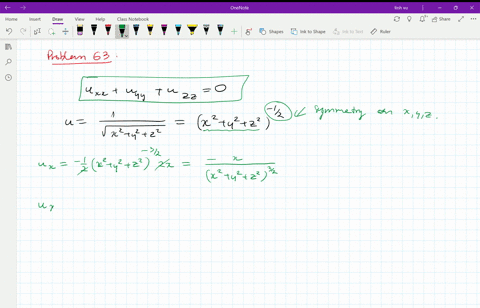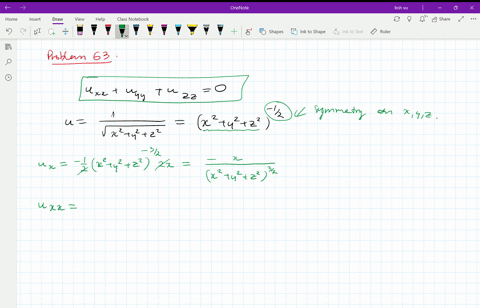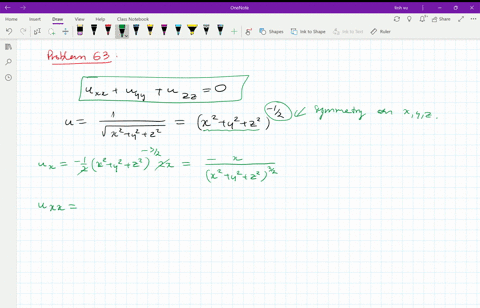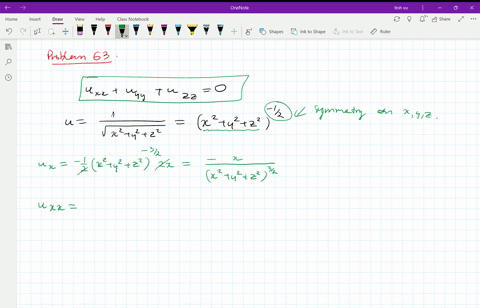 1 |  1 |
1 |  1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 | 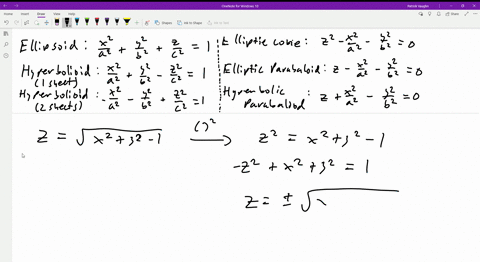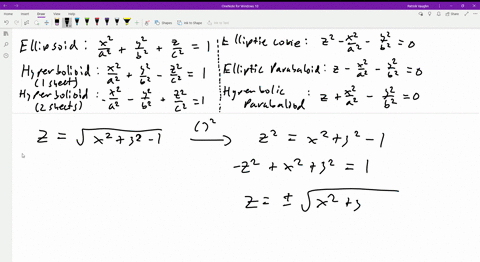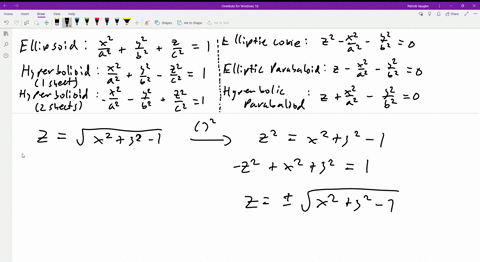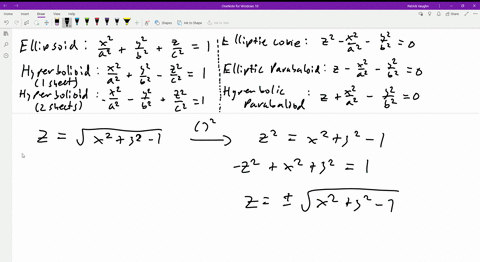 1 |
 1 |  1 |  1 |
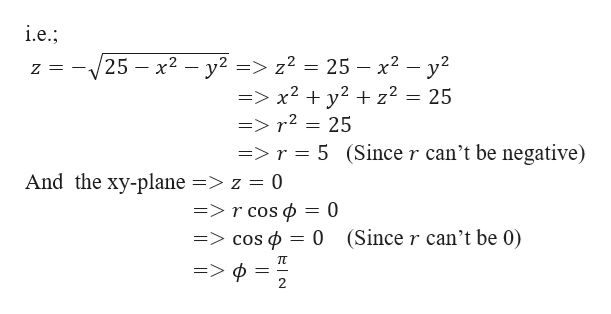 1 |  1 | 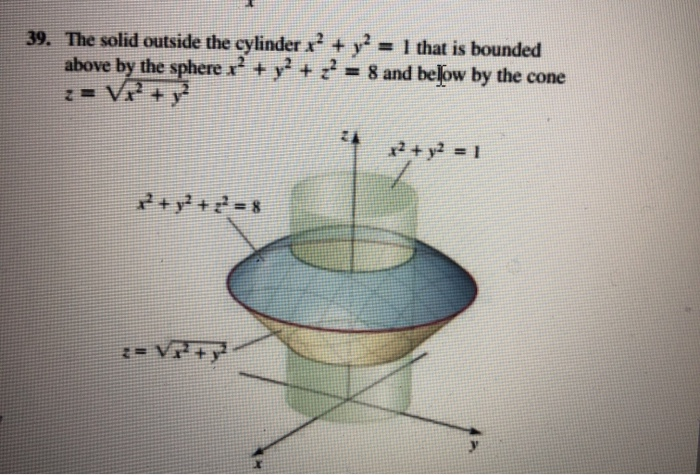 1 |
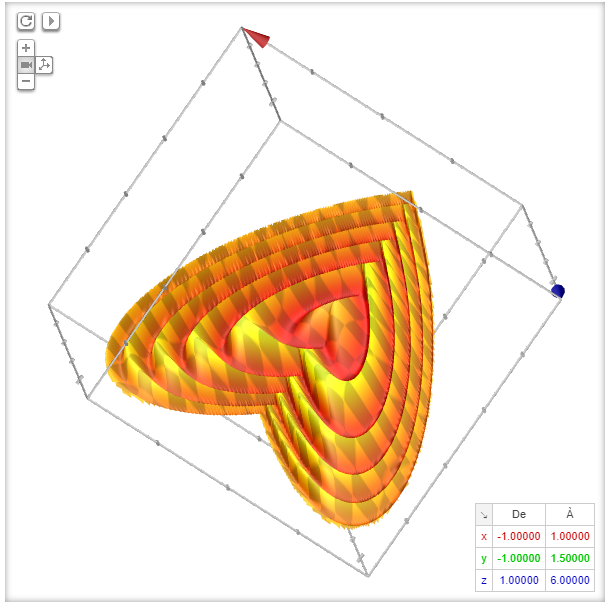 1 | 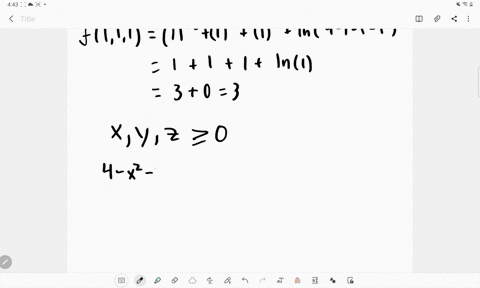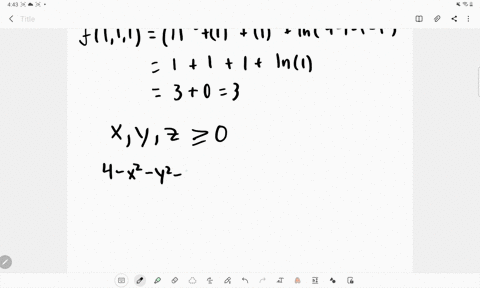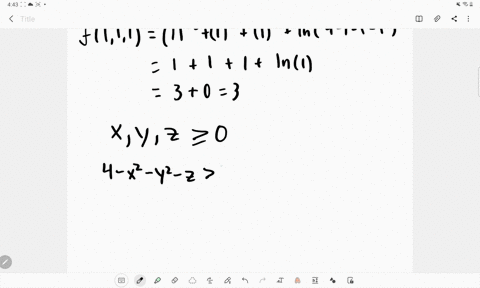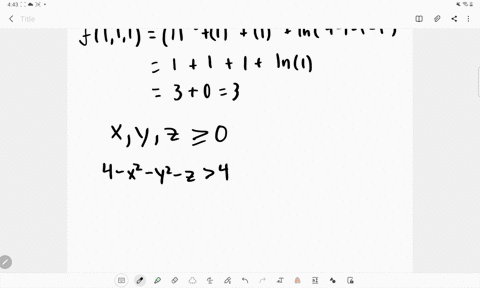 1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 | 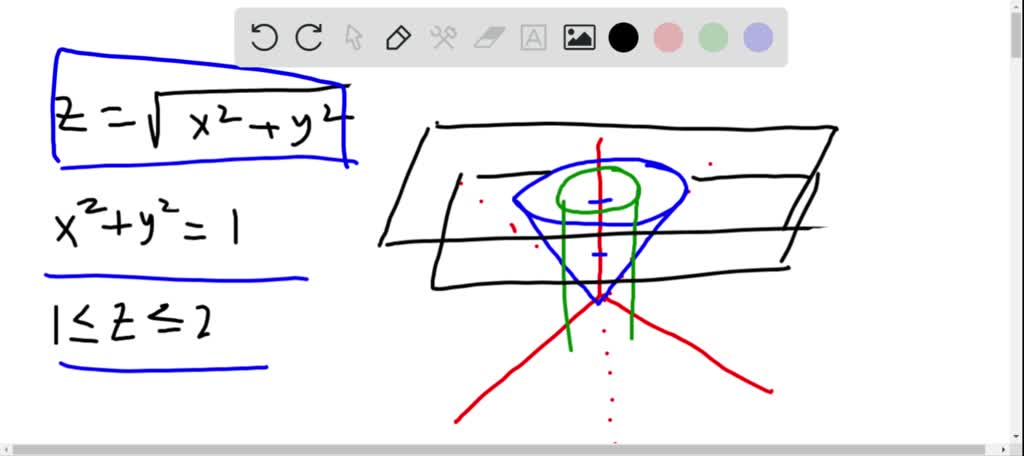 1 |
 1 | 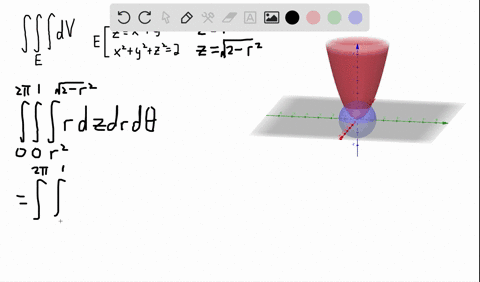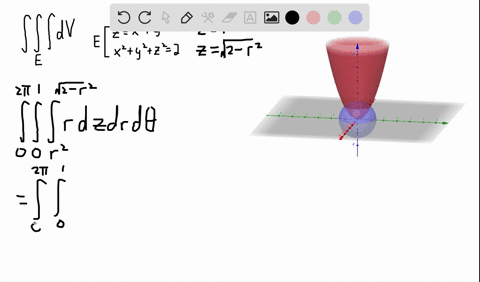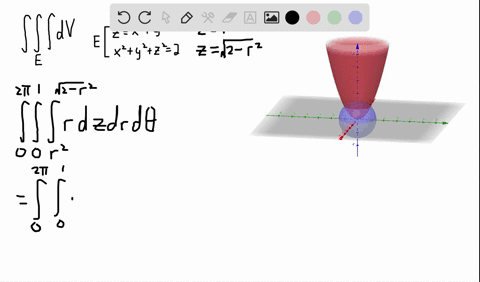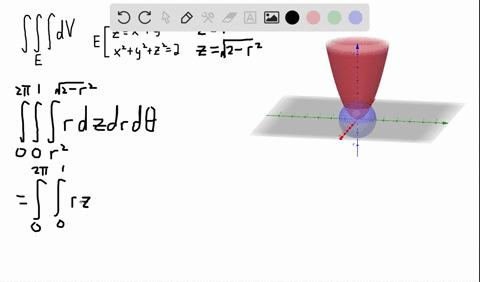 1 |  1 |
 1 | 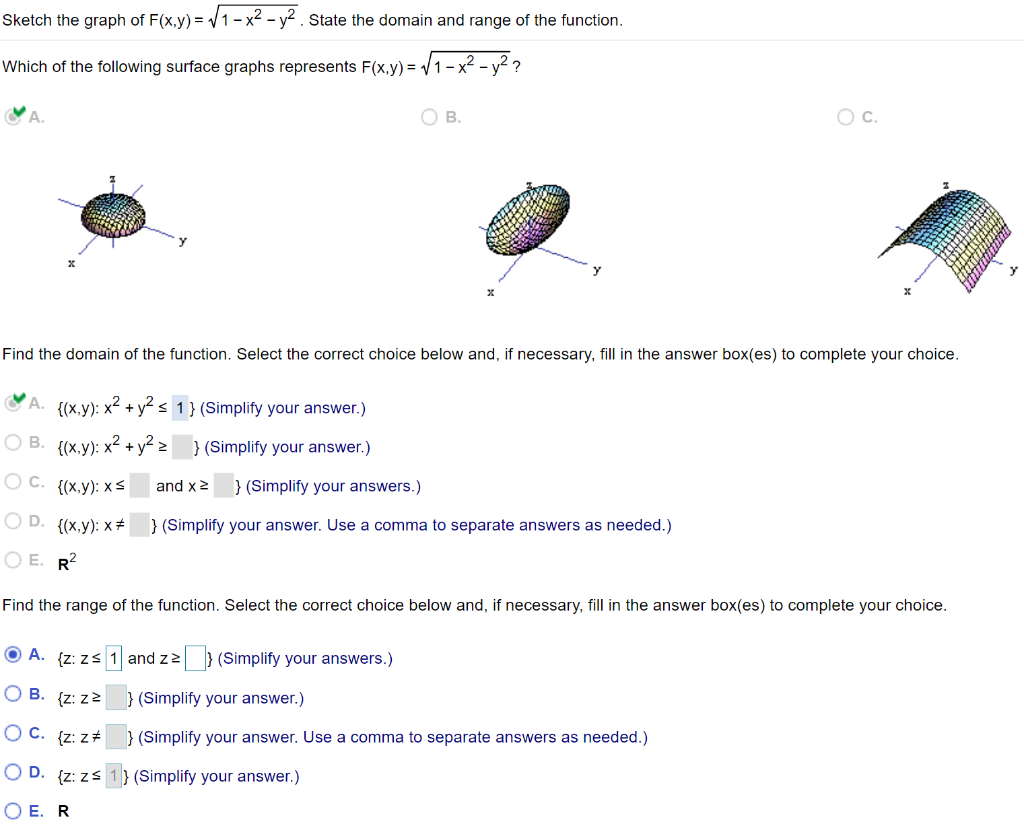 1 |  1 |
 1 | 1 |  1 |
 1 |  1 |
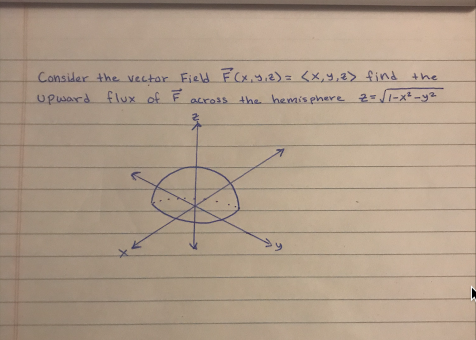
Find all first and second partial derivatives of z with respect to x and y if x^24y^216z^2−64=0 Trig Find the exact values of the six trigonometric functions 0 if the terminal side of 0 in standard position contains the points(5,4) (0 is not the number zero I don't know what its called) I have to find r first r=sqrt x^2y^2Find stepbystep Calculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question By about how much will $$ f ( x , y , z ) = \ln \sqrt { x ^ { 2 } y ^ { 2 } z ^ { 2 } } $$ change if the point P(x, y, z) moves from $$ P_0(3, 4, 12) $$ a distance of ds = 01 unit in the direction of $$ 3 \mathbf { i } 6 \mathbf { j } 2 \mathbf { k } ?
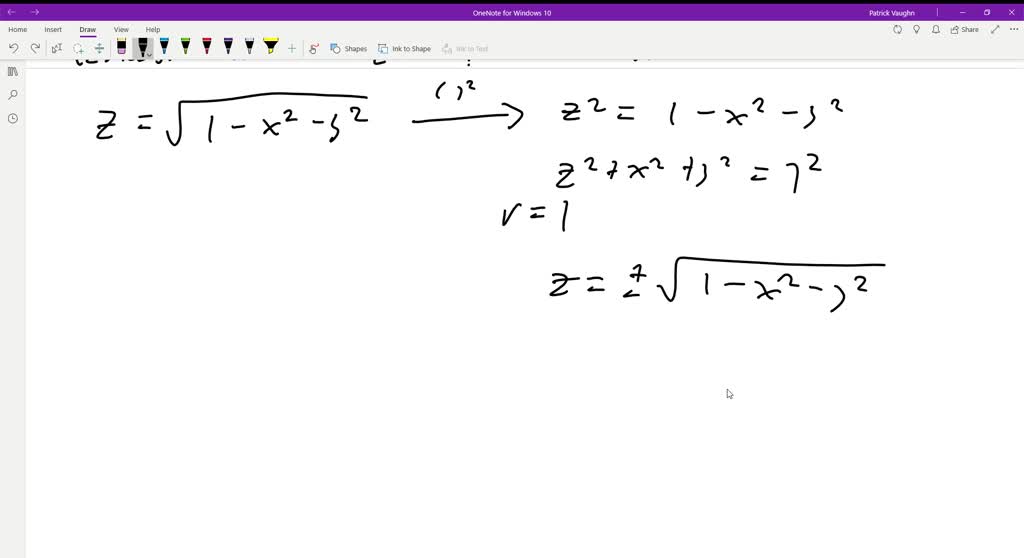
Incoming Term: z=sqrt(1-x^2-y^2), graph z=sqrt(1-x^2-y^2), u=1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), integral 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), laplacian of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), derivative of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), partial derivative of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), triple integral of 1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2), verify that the function y=1/sqrt(x^2+y^2+z^2),



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿